Is so3 a polyatomic ion – In the realm of chemistry, the question of whether SO3 is a polyatomic ion sparks curiosity and invites exploration. Polyatomic ions, captivating molecular entities, possess a unique structure and properties that set them apart in the chemical landscape. Embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of SO3, its molecular architecture, and its captivating chemical behavior.
SO3, a fascinating molecule, boasts a trigonal planar geometry, with three oxygen atoms symmetrically arranged around a central sulfur atom. The chemical bonds within SO3, a combination of covalent and dative bonds, contribute to its stability and shape its reactivity.
Delving deeper, we uncover the acidic nature of SO3, a property that renders it capable of forming sulfuric acid, a compound with widespread industrial applications.
Definition of a Polyatomic Ion
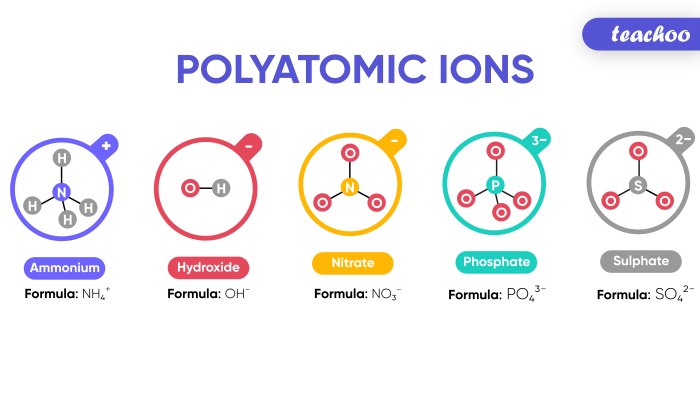
A polyatomic ion is an ion composed of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together. These ions carry an overall electric charge and behave as a single unit within chemical reactions. They are often found in ionic compounds, where they combine with oppositely charged ions to form electrically neutral compounds.
Structure of a Polyatomic Ion
Polyatomic ions consist of a central atom surrounded by other atoms or groups of atoms. The central atom typically has a higher electronegativity than the surrounding atoms, which means it attracts electrons more strongly. This uneven distribution of electrons creates an electric charge on the ion.
Properties of Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions have several characteristic properties:
- They carry an overall electric charge, either positive or negative.
- They behave as a single unit in chemical reactions.
- They can form ionic compounds with oppositely charged ions.
- They can exist in solution or as solids.
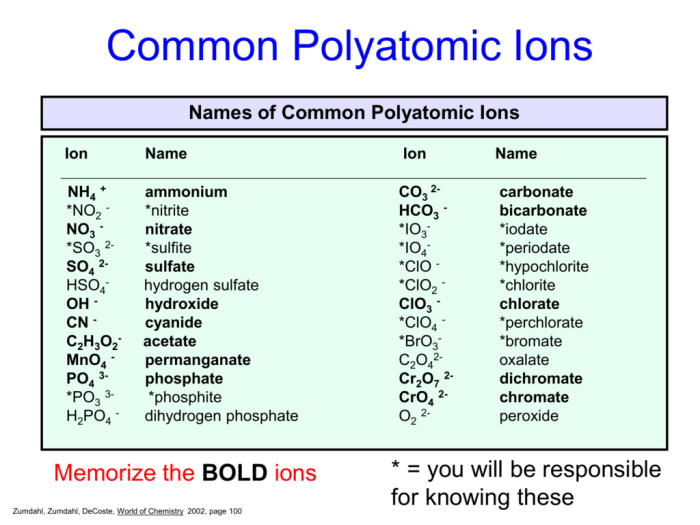
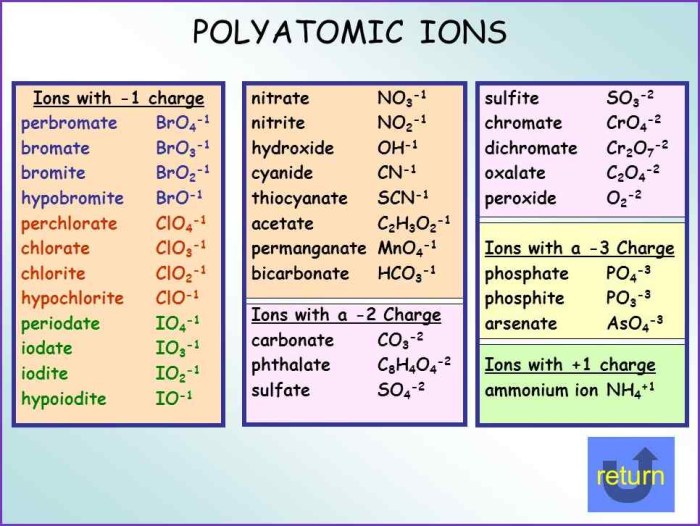
Common Polyatomic Ions
Some common polyatomic ions and their chemical formulas include:
- Hydroxide ion (OH –)
- Carbonate ion (CO 32-)
- Sulfate ion (SO 42-)
- Ammonium ion (NH 4+)
- Nitrate ion (NO 3–)
Structure and Bonding of SO3
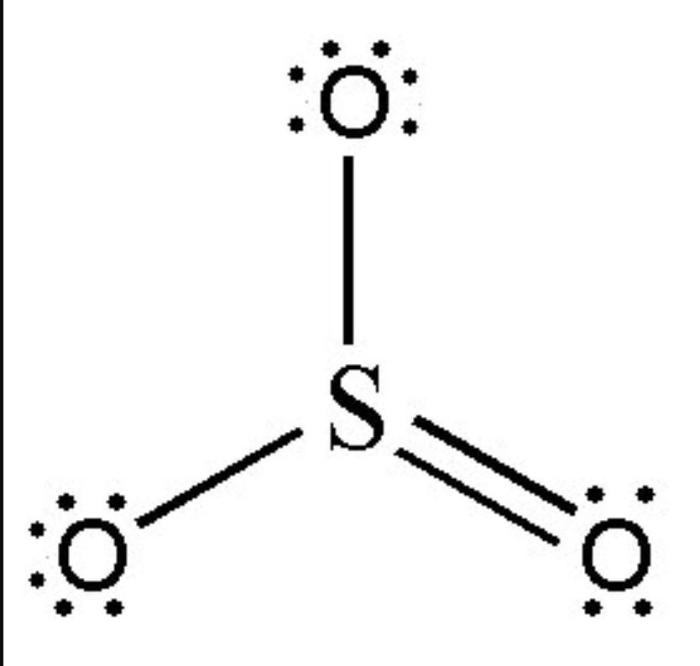
Sulfur trioxide (SO3) is a molecule with a trigonal planar molecular geometry. This means that the sulfur atom is at the center of the molecule, and the three oxygen atoms are arranged in a plane around it. The bond angles between the sulfur atom and the oxygen atoms are 120 degrees.
The chemical bonds in SO3 are covalent bonds. Each sulfur atom shares two electrons with each oxygen atom, forming a double bond. The double bonds between the sulfur atom and the oxygen atoms are very strong, which contributes to the stability of the SO3 molecule.
Resonance in SO3
The double bonds in SO3 can resonate between the three oxygen atoms. This means that the electrons in the double bonds can move around the molecule, and the bonds can be described as being spread out over all three oxygen atoms.
The resonance in SO3 helps to stabilize the molecule and makes it less reactive.
Properties of SO3: Is So3 A Polyatomic Ion
Sulfur trioxide (SO3) exhibits a range of physical and chemical properties that make it a versatile and reactive substance. Let’s delve into its characteristics:
Physical Properties
- SO3 exists as a colorless gas at room temperature.
- It has a pungent, choking odor.
- Its melting point is -16.8 °C (2.7 °F), and its boiling point is 44.5 °C (112.1 °F).
Chemical Properties, Is so3 a polyatomic ion
SO3 is highly reactive, readily reacting with water and other substances. Here are some key chemical properties:
Acidic Nature
SO3 is an acidic oxide, meaning it reacts with water to form a strong acid, sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
This reaction is highly exothermic, releasing a significant amount of heat.
SO3, or sulfur trioxide, is indeed a polyatomic ion, composed of one sulfur atom and three oxygen atoms. For those interested in studying more about medical and surgical topics, I highly recommend checking out this comprehensive med surg test bank pdf . Returning to our discussion on SO3, it plays a significant role in atmospheric chemistry, contributing to acid rain formation.
Reactivity with Bases
SO3 reacts with bases to form sulfites (SO32-) or sulfates (SO42-).
SO3 + 2NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2OSO3 + H2O + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Reactivity with Metals
SO3 reacts with some metals, forming sulfites or sulfates. For example:
SO3 + Fe → FeSO3
Applications of SO3
Sulfur trioxide (SO3) finds numerous industrial applications, particularly in the production of sulfuric acid, a crucial chemical used in various sectors.
Role in Sulfuric Acid Production
SO3 is the primary precursor for sulfuric acid (H2SO4) production via the contact process. In this process, SO2 is oxidized to SO3 in the presence of a catalyst, such as vanadium pentoxide (V2O5). The SO3 is then absorbed in concentrated sulfuric acid to form oleum (H2SO4·SO3), which is subsequently diluted to produce sulfuric acid.
Other Chemical Applications
Beyond sulfuric acid production, SO3 is also used in the manufacture of other chemicals, including:
- Sulfites and bisulfites: Used as preservatives and reducing agents in the food and beverage industry.
- Sulfuryl chloride (SO2Cl2): A reagent in organic synthesis and a fumigant.
- Chlorosulfonic acid (HSO3Cl): A sulfonating agent in the production of detergents and dyes.
Environmental and Health Impacts
While SO3 has significant industrial applications, its release into the environment poses potential risks:
- Acid Rain:SO3 reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid, a major component of acid rain. Acid rain can damage ecosystems, corrode infrastructure, and harm human health.
- Respiratory Issues:Exposure to SO3 can irritate the respiratory tract, causing coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Skin and Eye Irritation:Direct contact with SO3 can cause skin and eye irritation, including redness, itching, and burning sensations.
Therefore, proper emission controls and safety measures are crucial to mitigate the environmental and health impacts associated with SO3.
Question & Answer Hub
Is SO3 a monatomic ion?
No, SO3 is not a monatomic ion. It is a polyatomic ion, consisting of three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom.
What is the molecular geometry of SO3?
SO3 has a trigonal planar molecular geometry, with the three oxygen atoms arranged symmetrically around the central sulfur atom.
Is SO3 acidic or basic?
SO3 is acidic. It reacts with water to form sulfuric acid, a strong acid.
