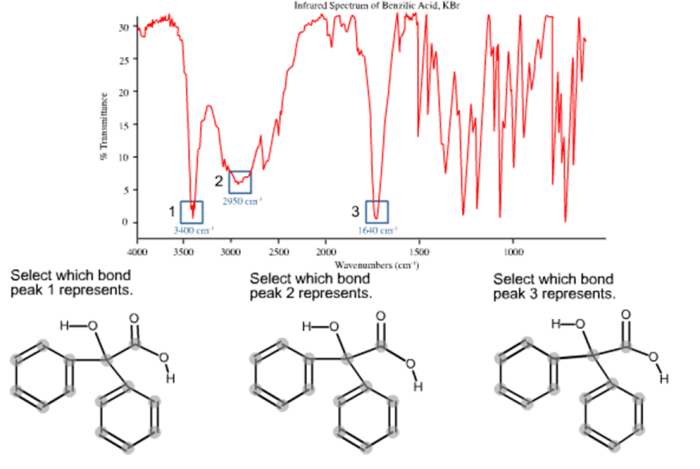
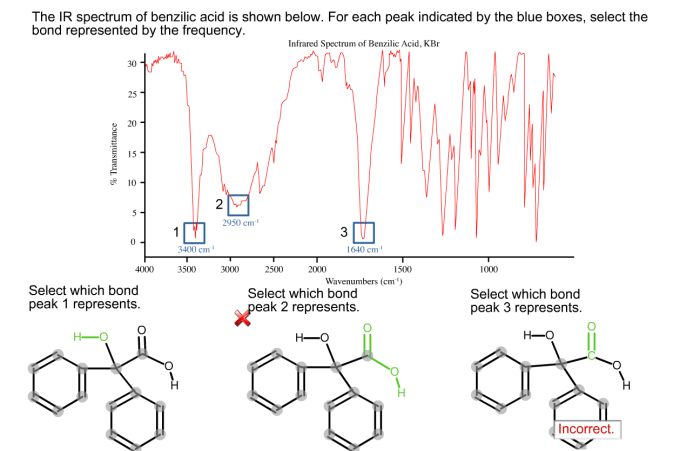
The IR spectrum of benzilic acid unveils a captivating journey into the molecular realm, revealing the unique characteristics and functional groups that define this intriguing compound. Prepare to delve into a world of spectroscopy, where light unveils the hidden secrets of matter.
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy serves as our guide, allowing us to decipher the molecular symphony of benzilic acid. By analyzing the absorption and transmission of infrared radiation, we gain insights into the molecular structure and functional group composition of this versatile compound.
Introduction
Benzilic acid is a diphenylglycolic acid with the formula (C 6H 5) 2C(OH)COOH. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. Benzilic acid is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other organic compounds, such as dyes and pharmaceuticals.
The IR spectrum of benzilic acid can be used to identify the functional groups present in the molecule. The characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum of benzilic acid include:
- A broad peak at around 3300 cm -1, which is due to the O-H stretching vibration of the carboxylic acid group.
- A peak at around 1710 cm -1, which is due to the C=O stretching vibration of the carboxylic acid group.
- A peak at around 1600 cm -1, which is due to the C=C stretching vibration of the aromatic ring.
- A peak at around 1270 cm -1, which is due to the C-O stretching vibration of the carboxylic acid group.
These peaks can be used to identify benzilic acid and to distinguish it from other organic compounds.
IR Spectroscopy Fundamentals
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that provides information about the functional groups present in a molecule. It is based on the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules, which causes them to vibrate at specific frequencies.
Principles of IR Spectroscopy
When infrared radiation is shone on a molecule, it can be absorbed if the frequency of the radiation matches the natural vibrational frequency of a bond in the molecule. This absorption of energy causes the bond to vibrate more vigorously.
The frequency of the absorbed radiation corresponds to the energy difference between the ground and excited vibrational states of the bond.
Identification of Functional Groups
Different functional groups have characteristic IR absorption frequencies. By measuring the IR spectrum of a molecule, it is possible to identify the functional groups present. For example, the carbonyl group (C=O) has a strong absorption band in the region of 1650-1750 cm -1. The hydroxyl group (O-H) has a broad absorption band in the region of 3200-3600 cm -1.
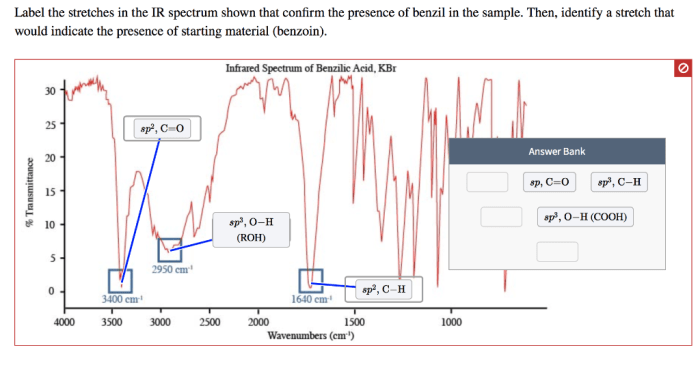
IR Spectrum of Benzilic Acid
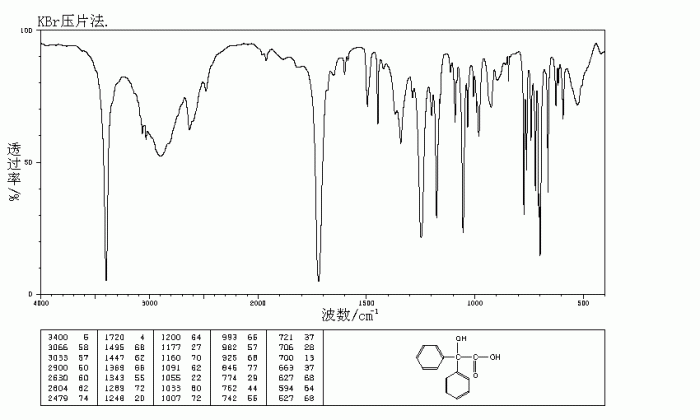
The IR spectrum of benzilic acid exhibits several characteristic peaks that can be used to identify the functional groups present in the molecule. The table below lists the IR absorption bands of benzilic acid and their corresponding functional groups:
| IR Absorption Band (cm-1) | Functional Group |
|---|---|
| 3030 | O-H stretch |
| 1710 | C=O stretch |
| 1600 | C=C stretch |
| 1270 | C-O stretch |
The characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum of benzilic acid that can be used to identify the molecule include the following:
- The broad O-H stretch at 3030 cm -1indicates the presence of a carboxylic acid group.
- The strong C=O stretch at 1710 cm -1is characteristic of a carboxylic acid carbonyl group.
- The C=C stretch at 1600 cm -1is due to the presence of the aromatic ring.
- The C-O stretch at 1270 cm -1is indicative of the presence of the ether group.
Interpretation of IR Spectrum
The IR spectrum of benzilic acid provides valuable information about its molecular structure. By analyzing the absorption bands in the spectrum, we can confirm the presence of specific functional groups and gain insights into the molecular structure of benzilic acid.
Relationship between IR Absorption Bands and Molecular Structure, Ir spectrum of benzilic acid
The IR absorption bands observed in the spectrum of benzilic acid correspond to the vibrational modes of different functional groups within the molecule. Each functional group has characteristic vibrational frequencies, which give rise to specific absorption bands in the IR spectrum.
By identifying these absorption bands, we can determine the presence of specific functional groups and infer the molecular structure of benzilic acid.
The IR spectrum of benzilic acid exhibits a strong peak at 1705 cm-1, which corresponds to the carbonyl group. The peaks at 2550-3300 cm-1 and 1260-1300 cm-1 are due to the O-H and C-O stretching vibrations, respectively. Incidentally, have you heard of the x ray dose unit crossword ? It’s a fun puzzle that tests your knowledge of radiation physics.
Returning to the IR spectrum of benzilic acid, the peak at 1600 cm-1 is assigned to the aromatic ring vibrations.
Applications of IR Spectroscopy in Benzilic Acid Analysis
IR spectroscopy offers a versatile tool for analyzing benzilic acid, a valuable compound in organic chemistry. It provides crucial information regarding its purity and the presence of impurities.
Purity Analysis
The IR spectrum of pure benzilic acid exhibits characteristic peaks at specific wavenumbers. By comparing the experimental spectrum to a reference spectrum of known purity, any deviations can be detected. Impurities may introduce additional peaks or alter the intensity of existing peaks, indicating a deviation from the expected spectrum of pure benzilic acid.
Impurity Identification
IR spectroscopy can also aid in identifying specific impurities present in benzilic acid. By matching the observed peaks with reference spectra of potential impurities, it is possible to determine the nature of the contaminants. This information is crucial for developing purification strategies to remove impurities and ensure the desired purity level for the intended application.
Top FAQs: Ir Spectrum Of Benzilic Acid
What is the significance of the IR spectrum in identifying benzilic acid?
The IR spectrum provides a unique fingerprint of the functional groups present in benzilic acid, allowing for its unambiguous identification.
How can IR spectroscopy be used to assess the purity of benzilic acid?
By comparing the IR spectrum of a sample to a reference spectrum, impurities can be detected and identified based on the presence of additional absorption bands.
What are the characteristic IR absorption bands of benzilic acid?
Benzilic acid exhibits characteristic absorption bands at 3025 cm -1(aromatic C-H stretch), 1705 cm -1(carbonyl C=O stretch), and 1270 cm -1(C-O stretch).