Which of the following statements is true of antigen-antibody interactions – As the topic of antigen-antibody interactions takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with meticulous precision, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the intricacies of immune responses, this discourse unravels the fundamental principles governing the interplay between antigens and antibodies, illuminating their profound implications in health and disease.
The ensuing paragraphs provide a comprehensive exploration of antigen-antibody interactions, encompassing their specificity, role in immune responses, and clinical applications. Through a lucid and engaging narrative, readers will gain a deep understanding of these fundamental immunological processes, empowering them to navigate the complexities of the immune system with confidence.
Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Antigen-antibody Interactions
Antigen-antibody interactions are fundamental to the immune system’s ability to recognize and respond to foreign invaders. These interactions play a crucial role in the development of adaptive immunity, which allows the immune system to mount specific and long-lasting responses to specific pathogens.
Role of Antigens and Antibodies in the Immune System
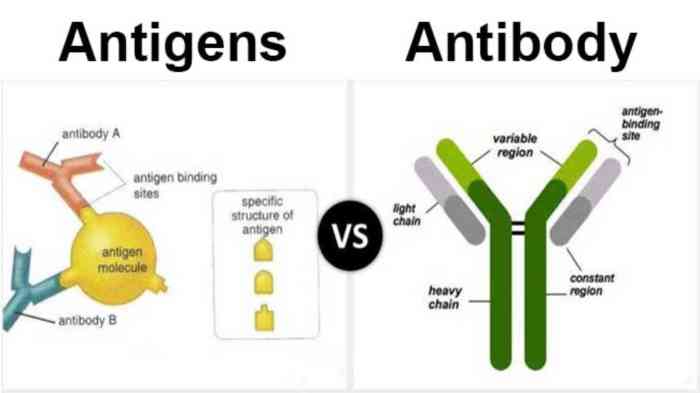
- Antigens are foreign substances that trigger an immune response. They can be proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, or nucleic acids derived from pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
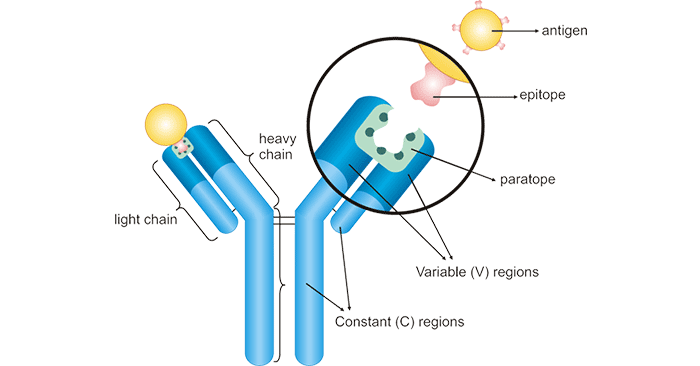
- Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by B cells in response to an antigen. Each antibody has a unique structure that allows it to bind to a specific antigen, like a key fitting into a lock.
Specificity of Antigen-Antibody Interactions
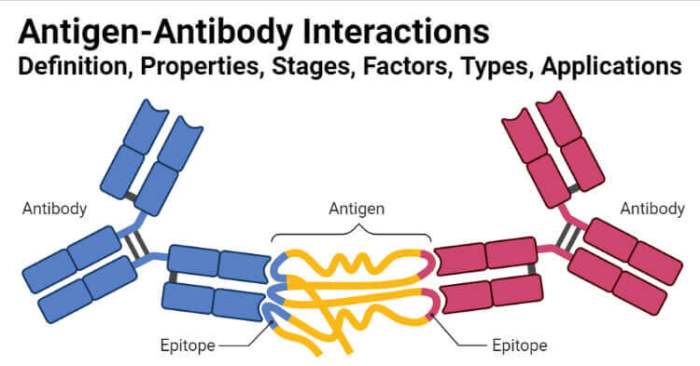
The specificity of antigen-antibody interactions is achieved through the concept of epitope-paratope binding. Each antigen has multiple epitopes, which are specific regions that can be recognized by antibodies. Antibodies, in turn, have paratopes, which are complementary to specific epitopes on the antigen.
This specificity ensures that antibodies can bind to their target antigens with high affinity, allowing for precise recognition and targeting of foreign invaders.
Role of Antigen-Antibody Interactions in Immune Responses
Antigen-antibody interactions trigger immune responses by:
- Neutralization: Antibodies can bind to and neutralize toxins or viruses, preventing them from infecting cells.
- Opsonization: Antibodies can coat antigens, making them more recognizable to phagocytic cells, which engulf and destroy them.
- Complement activation: Antibodies can activate the complement system, a group of proteins that work together to kill pathogens.
Clinical Applications of Antigen-Antibody Interactions, Which of the following statements is true of antigen-antibody interactions
Antigen-antibody interactions have numerous clinical applications:
- Diagnostic tests: Antibodies can be used to detect the presence of specific antigens in the body, aiding in the diagnosis of infections or autoimmune diseases.
- Therapeutic applications: Monoclonal antibodies, which are antibodies produced in the laboratory that target specific antigens, are used to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of antibodies?
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, play a crucial role in the adaptive immune response by specifically binding to and neutralizing foreign antigens, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
How does the specificity of antigen-antibody interactions contribute to immune function?
The exquisite specificity of antigen-antibody interactions ensures that the immune system can distinguish between self and non-self, enabling it to target and eliminate foreign invaders while preserving the integrity of host tissues.
What are the different types of antigen-antibody interactions?
Antigen-antibody interactions can be classified into various types based on the nature of the antigen and antibody involved, including direct binding, agglutination, precipitation, and complement activation.