Ancient near east map quiz – Embark on an adventure through the ancient Near East with our captivating map quiz! This interactive experience invites you to navigate the region’s diverse landscapes, unravel its rich history, and discover the civilizations that shaped the world as we know it.
Prepare to traverse vast deserts, navigate mighty rivers, and explore bustling cities as you test your knowledge of this fascinating era. Let’s embark on a journey where history and geography intertwine, offering a glimpse into the past that continues to resonate today.
Ancient Near East Geography
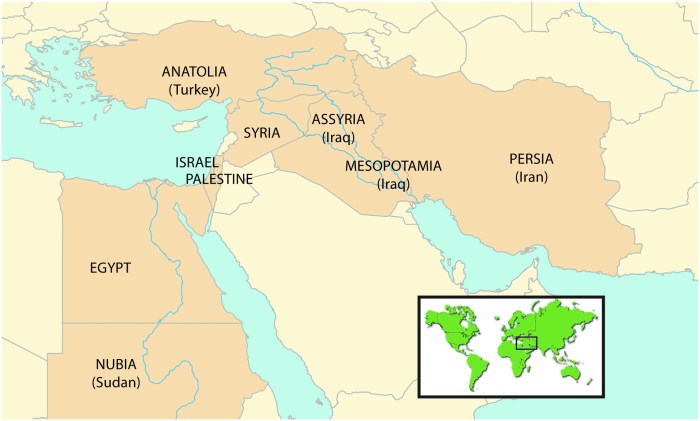
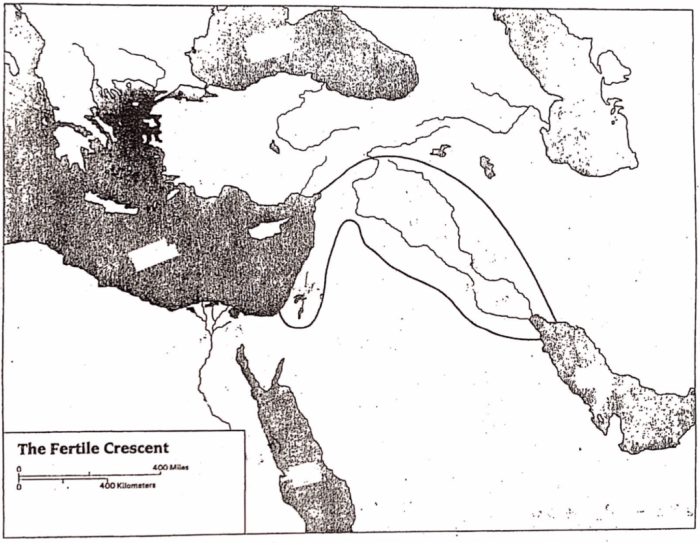
The ancient Near East, often known as the cradle of civilization, is a historical region encompassing the lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea and the Persian Gulf. Geographically, it stretches from the Nile River in Egypt in the west to the Indus River in Pakistan in the east, and from the Caucasus Mountains in the north to the Arabian Desert in the south.
Major Rivers
Two major rivers played a vital role in the development of ancient Near Eastern civilizations: the Nile River in Egypt and the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Mesopotamia. These rivers provided water for irrigation, transportation, and trade, and their fertile floodplains were ideal for agriculture.
Mountain Ranges
The ancient Near East is also home to several significant mountain ranges. The Taurus Mountains in southern Turkey and the Zagros Mountains in western Iran formed natural barriers between different regions and influenced the movement of people and goods.
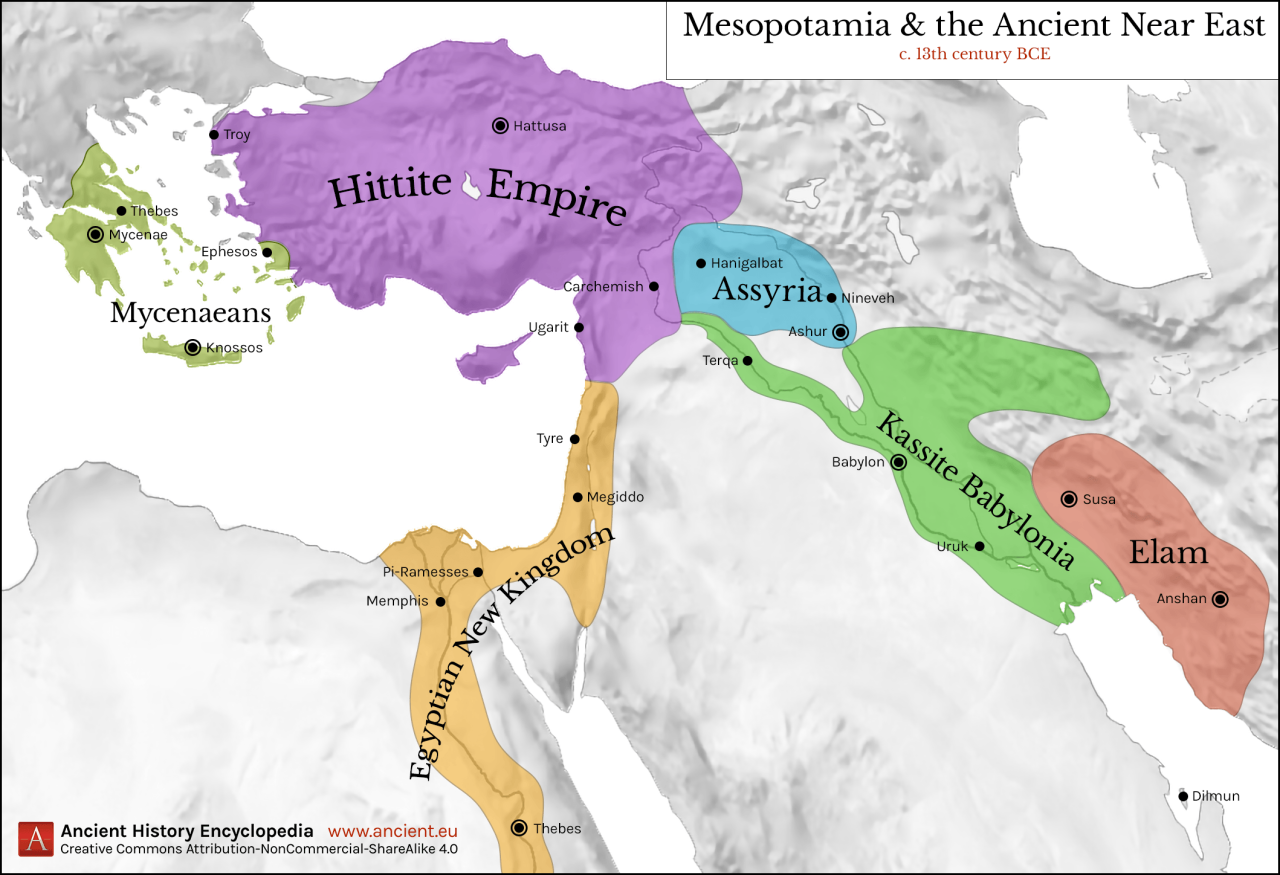
Map of the Ancient Near East
The map below shows the major cities and regions of the ancient Near East, including Egypt, Mesopotamia, Anatolia, and the Levant. It also includes the locations of the Nile River, Tigris River, Euphrates River, Taurus Mountains, and Zagros Mountains.
[Insert map of the ancient Near East with labeled cities and regions here]
Take a break from the ancient near east map quiz and delve into the complexities of ac theory level 2 lesson 5 here . Once you’ve mastered the nuances of ac theory, return to the ancient near east map quiz to conquer those elusive locations.
Ancient Civilizations of the Near East
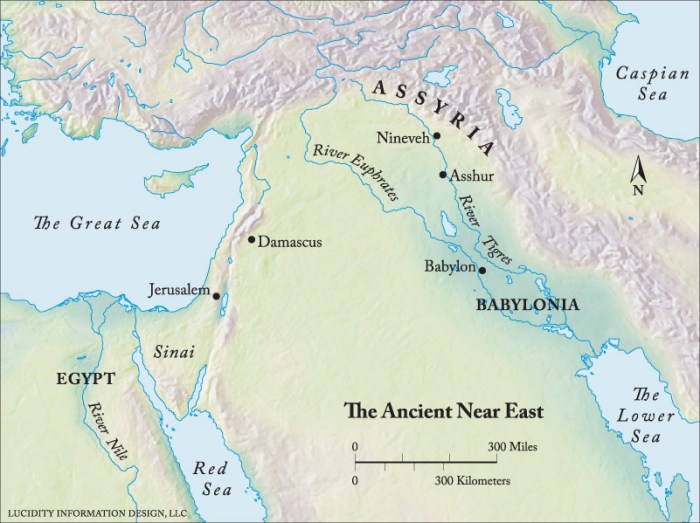
The Near East, a region of immense historical significance, was the cradle of several ancient civilizations that made profound contributions to human development. From the fertile plains of Mesopotamia to the deserts of Egypt, these civilizations flourished, leaving behind a legacy that continues to shape our world today.
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, meaning “land between rivers,” is the birthplace of some of the world’s earliest civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These civilizations developed advanced systems of writing, mathematics, and astronomy, and their cities were centers of trade and cultural exchange.
- Sumerians:The Sumerians, who flourished from around 4500 BCE, are credited with inventing the first known written language, cuneiform, and with developing a sophisticated system of irrigation that transformed the region into a fertile agricultural heartland.
- Babylonians:The Babylonians, who emerged around 2000 BCE, built the legendary city of Babylon, one of the largest and most advanced cities of the ancient world. They are known for their contributions to astronomy, including the development of a calendar based on the lunar cycle, and for their code of laws, the Code of Hammurabi, which set forth principles of justice and equality.
- Assyrians:The Assyrians, who rose to power in the 14th century BCE, established a vast empire that stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. They were renowned for their military prowess and their use of siege warfare, which enabled them to conquer and control a vast territory.
Egypt
Ancient Egypt, located along the fertile banks of the Nile River, developed one of the most enduring and influential civilizations in history. The Egyptians were masters of architecture, engineering, and mathematics, and their culture and beliefs have had a profound impact on Western civilization.
- Old Kingdom:The Old Kingdom period (c. 2686-2181 BCE) saw the construction of the Great Pyramids of Giza, a testament to the architectural prowess and engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians.
- Middle Kingdom:The Middle Kingdom period (c. 2055-1650 BCE) was a time of cultural and economic prosperity. The Egyptians expanded their empire, developed a system of hieroglyphic writing, and made significant advancements in mathematics and astronomy.
- New Kingdom:The New Kingdom period (c. 1550-1069 BCE) was a time of military conquest and territorial expansion. The Egyptians conquered Nubia to the south and established control over parts of the Near East. This period also saw the construction of some of the most famous temples and tombs in Egypt, including the Temple of Karnak and the Valley of the Kings.
Other Civilizations
In addition to Mesopotamia and Egypt, several other civilizations flourished in the Near East, each making its own unique contributions to human history.
- Hittites:The Hittites, who emerged in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) around 1600 BCE, were skilled metalworkers and military tacticians. They developed a system of writing known as cuneiform and played a significant role in the political landscape of the Near East.
- Canaanites:The Canaanites, who inhabited the region of Canaan (modern-day Israel and Palestine) from around 3000 BCE, were a maritime people who engaged in trade and cultural exchange throughout the Mediterranean. They developed a written language known as Phoenician, which later became the basis for the Greek and Latin alphabets.
- Persians:The Persians, who emerged in the 6th century BCE, established a vast empire that stretched from the Indus River to the Mediterranean Sea. They were known for their administrative skills, their system of roads and communication, and their religious beliefs, which influenced the development of Zoroastrianism.
Ancient Near East Culture
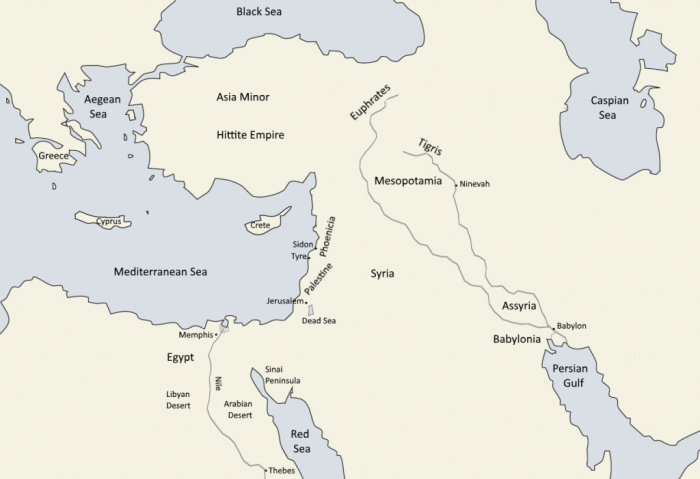
The ancient Near East was a cradle of civilization, where some of the world’s earliest and most influential cultures emerged. These cultures left a lasting legacy in terms of religion, art, architecture, writing, and education.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
The people of the ancient Near East had a variety of religious beliefs and practices. They believed in many gods and goddesses, who were often associated with natural phenomena such as the sun, moon, and stars. They also believed in an afterlife, where the dead would be judged according to their actions in life.Religious
rituals and ceremonies were an important part of ancient Near Eastern society. These rituals were often performed in temples, which were often elaborate and decorated with religious symbols.
Art and Architecture, Ancient near east map quiz
The art and architecture of the ancient Near East was influenced by the religious beliefs of the people. Temples and palaces were often decorated with reliefs and statues depicting gods and goddesses, as well as scenes from mythology.The ancient Near East was also home to some of the world’s earliest writing systems.
The first known writing system, cuneiform, was developed in Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE. Cuneiform was used to write on clay tablets, which were used for a variety of purposes, including recording laws, religious texts, and economic transactions.
Role of Writing and Education
Writing and education played an important role in ancient Near Eastern society. Schools were established to teach students how to read and write. These schools were often attached to temples or palaces.The ability to read and write was highly valued in ancient Near Eastern society.
Scribes were often employed by the government or by wealthy individuals to write letters, contracts, and other documents.
Ancient Near East Trade and Economy: Ancient Near East Map Quiz
The ancient Near East was a hub of trade and commerce, with major trade routes connecting the region to other parts of the world. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, contributing to the development of sophisticated economic systems.
Major Trade Routes
- Royal Road:Connected Susa in Persia to Sardis in Lydia, spanning over 1,500 miles.
- Silk Road:Originating in China, it extended west through Central Asia and the Near East, facilitating the trade of silk, spices, and other luxury goods.
- Spice Route:Linked the Arabian Peninsula to India and Southeast Asia, primarily for the trade of spices, incense, and precious stones.
Agricultural Practices and Economic Systems
Agriculture was the foundation of the Near Eastern economy. The region’s fertile river valleys, such as the Nile and Tigris-Euphrates, supported extensive farming and irrigation systems. Common crops included wheat, barley, olives, and dates.
Economic systems varied across the region. Some areas, like Mesopotamia, developed centralized economies with a ruling class controlling land and resources. Others, like Egypt, had a more decentralized system with independent farmers and artisans.
Money and Finance
The use of money and finance emerged in the ancient Near East around the 3rd millennium BCE. Early forms of currency included barley, silver, and gold. The development of writing systems allowed for the recording of financial transactions and the emergence of banking practices.
Helpful Answers
What is the geographic scope of the ancient Near East?
The ancient Near East encompasses the region from the eastern Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf, including present-day Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Iran.
Name the major ancient civilizations of the Near East.
The major ancient civilizations of the Near East include Mesopotamia (Sumer, Akkad, Babylonia, Assyria), Egypt, Anatolia (Hittites), Persia (Medes, Persians), and Phoenicia.
What were some of the key contributions of ancient Near Eastern civilizations?
Ancient Near Eastern civilizations made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, writing, architecture, art, and religion, laying the foundation for many aspects of modern civilization.